Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Importance of balancing freedom of expression and content regulations in the metaverse
- Emerging legal and ethical challenges
- Metaverse and Its Features
2.1. Definition and Characteristics
2.2. Underlying Technologies- Web 3.0 and Blockchain
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
2.3. Applications of the Metaverse - Social
- Economic
- Educational and Research
- Entertainment and Creativity
- The Role of the Metaverse in Social and Economic Development
- Reducing geographical distances
- Creating new economic opportunities
- Challenges in Content Management in the Metaverse
4.1. Illegal and Harmful Content- Cybercrimes
- Virtual harassment
- Inappropriate content
4.2. Technical Complexities - Real-time synchronization
- Large-scale scalability
4.3. Ethical Issues - User privacy
- Cultural diversity
- Transparency and accountability
- Legal Regulations and Frameworks
5.1. Existing Laws- The European Union Digital Services Act (DSA)
- National initiatives
5.2. Legal Gaps - Absence of specific regulations for the metaverse
- Complexity of decentralized architectures
- Legal conflicts between countries
5.3. Recommendations for New Legislation - Establishing international frameworks
- Developing advanced regulatory technologies
- Strengthening global cooperation
- Impact of International Law on the Metaverse
- Harmonizing global regulations
- Combating cyber threats
- Practical Solutions for Balancing Freedom of Expression and Content Regulations
7.1. Leveraging Advanced Technologies- AI and machine learning
- User-driven reporting systems
- Big data analysis
- Blockchain systems
7.2. Developing Transparent and Comprehensive Policies - Clear guidelines for users
- Periodic reports
7.3. Supporting User and Content Moderator Well-being - Training programs for moderators
- Establishing support structures
- Psychological tools
7.4. Educating and Raising Awareness Among Users - Online risks and responsibilities
- Conclusion
- Emphasizing the necessity of balancing freedom of expression and security
- Proposals for the future of the metaverse
Introduction
In the digital age, striking a balance between freedom of expression and the need to create a safe environment for users has emerged as a significant legal and social challenge, particularly on metaverse platforms and Web 3.0-based technologies. The metaverse, as a virtual space enabling three-dimensional and immersive interactions, introduces new issues in content management and freedom of expression. This article examines the legal and ethical challenges in regulating content in the metaverse and proposes potential solutions.
The Metaverse and Its Features
Definition and Characteristics
The metaverse is a virtual and digital world created through modern technologies, offering users realistic and interactive experiences. This space is accessed not only via hardware such as virtual reality (VR) headsets and augmented reality (AR) glasses but also through environments where users can participate using their digital avatars, enabling diverse interactions.
This technology is widely utilized in areas such as online gaming, social communication, education, and commerce, introducing new possibilities for human interaction. Avatars, representing users’ digital identities, allow individuals to express themselves in various ways within virtual environments.
Underlying Technologies
- Web 3.0 and Blockchain:
Web 3.0, recognized as the next generation of the internet, enables data ownership to be transferred to users through decentralized architectures. Blockchain, a system for recording information that is tamper-proof, enhances the security of online transactions and interactions within the metaverse. These technologies allow individuals to maintain direct control over their digital identities, preventing unauthorized access. - Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
These technologies form the foundation of the metaverse experience. Virtual Reality (VR) creates fully simulated environments that users can access through specialized devices like headsets. In contrast, Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, offering interactive experiences. - Artificial Intelligence (AI):
The role of AI in the metaverse is rapidly expanding. AI can identify suspicious behaviors, generate intelligent content, and predict user actions. Leveraging AI for big data analysis enhances the personalization of user experiences within this space.
Applications of the Metaverse
Given its vast potential, the metaverse has found applications in various fields:
- Social:
Metaverse platforms enable users to connect in virtual spaces, attend meetings and conferences, and engage in social interactions. This feature is especially beneficial for individuals living in different parts of the world who cannot meet physically. - Economic:
The metaverse fosters a digital economy involving the trade of virtual goods, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and cryptocurrencies. Many users generate income by trading these items, creating new digital markets that sometimes surpass real-world ones. - Educational and Research:
The metaverse allows for highly interactive and realistic educational environments. This space can provide richer educational experiences, particularly in complex fields such as medicine, engineering, and social sciences. - Entertainment and Creativity:
Numerous games and recreational activities have been developed in the metaverse. Additionally, artists and designers can create digital artworks in this space, which has led to the emergence of new markets for digital art.
The Role of the Metaverse in Social and Economic Development
The metaverse can have significant impacts on social and economic aspects. By enabling users to interact from anywhere in the world, it reduces geographical distances and creates new economic opportunities. For instance, individuals can attend business meetings and conferences without traveling, while those in remote areas gain access to global markets.
Challenges of Content Management in the Metaverse
Illegal and Harmful Content
Monitoring and managing illegal and harmful content in the metaverse is highly complex. Since interactions occur online and in real time, identifying and addressing harmful or malicious content instantly is challenging. Illegal and harmful content includes the following:
- Cybercrimes: Ensuring users in the metaverse are not exposed to cyberattacks such as hacking and fraud is a significant challenge.
- Virtual Harassment: Particularly in social metaverses, there is a potential for sexual and psychological harassment through avatars, which is especially concerning when avatars represent users’ identities.
- Inappropriate Content: The dissemination of content that may be offensive to certain cultures or misleading poses another challenge.
Technical Complexities
- Real-time Synchronization: Many interactions within the metaverse occur in real time, adding significant complexity to content management. Traditional tools are often insufficient for identifying and swiftly removing harmful content in such dynamic environments.
- Large-scale Operations: Metaverse platforms, capable of hosting thousands or even millions of users simultaneously, require immense computational resources for effective content moderation and management.
Ethical Concerns
- User Privacy: Collecting and utilizing personal data in the metaverse can lead to privacy violations. Privacy laws and standards must be strictly defined and aligned with global regulations.
- Cultural Diversity: Content generated in the metaverse must respect cultural diversity to avoid misunderstandings or potential offenses across various cultures.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring the transparency and accountability of service providers is a core challenge in content moderation. Platforms should establish clear monitoring processes and communicate regularly with users about their content policies.
Legal Regulations and Frameworks
Existing Laws
- EU Digital Services Act (DSA): This legislation emphasizes the removal of illegal content from platforms, requiring digital companies to implement strict policies to prevent the spread of harmful materials.
- National Regulations: In addition to international laws, many countries have developed their own regulations for online platforms, addressing issues such as freedom of speech, data protection, and cybersecurity.
Legal Gaps
- Lack of Metaverse-specific Laws: Many countries and regions do not yet have regulations tailored to content moderation in the metaverse.
- Challenges of Decentralized Architectures: Since some metaverse platforms operate on decentralized systems, enforcing regulations becomes more complex.
- Legal Conflicts Across Countries: Diverse and sometimes conflicting regulations across nations create hurdles for harmonizing global standards and policies.
Recommendations for New Legislation
To balance freedom of expression and user safety in the metaverse, the following recommendations can be considered:
- Establishing international frameworks for metaverse governance.
- Developing AI-powered monitoring technologies.
- Strengthening global cooperation to combat cybercrimes.
- Using smart contracts to ensure compliance with intellectual property and legal requirements.
The Role of International Law in the Metaverse
International cooperation plays a vital role in aligning regulations and creating global standards for metaverse content management. Effective governance of spaces like the metaverse requires worldwide coordination to protect users from threats and harmful content.
Practical Solutions for Balancing Free Speech and Content Moderation
Balancing freedom of expression with content regulations on metaverse platforms is crucial. While users should have the right to express their opinions freely, harmful, illegal, or damaging content must be controlled to create a safe and healthy environment for everyone. The following practical solutions can help companies and organizations operating within the metaverse achieve this balance:
Advanced Technologies for Content Management
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning are among the most effective tools for managing content in the metaverse. These technologies can automatically identify and remove illegal or harmful materials. For instance, AI algorithms can detect images or videos containing violence, hate speech, or harassment and take immediate action to block or delete them. Machine learning systems can continuously analyze user behavior to identify patterns of illegal or harmful activities.
User-driven Reporting Systems:
Implementing user reporting systems allows individuals to quickly flag inappropriate content. These systems act as a supplementary tool alongside AI technologies to identify harmful materials. User reports can include inappropriate comments, images, or videos, which are then reviewed thoroughly by experts.
Big Data Analytics:
Big data analytics can identify harmful behavioral patterns among users. This is especially useful for tackling issues such as virtual harassment, discrimination, or offensive language. By analyzing large volumes of user-generated data, algorithms can effectively detect unauthorized content and take necessary actions.
Blockchain-based Transparency:
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency in content management processes. Many metaverse platforms already use blockchain to register and verify ownership of content and information. By leveraging blockchain, all changes and actions related to user content can be recorded transparently and immutably in public ledgers. This helps ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the decisions made, fostering trust.
Developing Transparent and Comprehensive Policies for Users
Clear Guidelines for Users:
One of the primary strategies for balancing freedom of speech and content regulations is to create clear and transparent user policies. These guidelines should explicitly outline what types of content are permissible and what are prohibited. For example, policies can detail restrictions on violent, discriminatory, or harassing content and clarify how such materials will be addressed. Additionally, these policies must be regularly updated to stay aligned with technological advancements and legal requirements.
Providing Periodic and Transparent Reports:
Metaverse companies and platforms must regularly provide reports detailing content management and the measures taken to ensure user safety and privacy. These reports should include the number of content items removed, content type, reasons for removal, and transparency in oversight processes. This approach builds user trust in the platform and alleviates concerns about freedom of speech violations.
Supporting the Well-being of Users and Content Moderators
Specialized Training for Content Moderators:
Content moderators play a crucial role in maintaining a balance between freedom of expression and regulations in metaverse platforms. Continuous, specialized training is essential for these individuals, covering topics such as identifying harmful content, handling complex cases, and respecting user rights. Moderators should also be well-versed in modern tools and technologies for content review and management.
Establishing Support Systems for Moderators:
Content moderators often face high stress, particularly when managing sensitive or challenging content. Creating support structures, including psychological support teams and assistive tools, can prevent burnout and improve decision-making quality.Psychological Tools for Supporting Victimized Users:
Some users may face harassment or harmful behaviors in the metaverse. Providing psychological tools such as online counseling, support systems, and educational resources can help affected users prevent psychological harm and cope more effectively with their experiences.
Educating and Raising Awareness Among Users
User Education on Online Risks and Responsibilities:
A key step in managing content and freedom of expression is educating users about the risks of the metaverse and their responsibilities. This education should be ongoing and accessible, covering topics like metaverse content rules, identifying harmful content, and strategies for addressing it.
Parental and Educator Awareness:
Given the metaverse’s appeal and complexity for children and teenagers, raising awareness among parents and educators about safe usage is vital. Parents should understand potential risks and how to monitor and guide their children effectively in these virtual spaces.
Developing Awareness Programs on Digital Rights:
Educational programs on users’ digital rights must also be established to inform individuals about their online rights and how to defend them. These programs can cover topics like privacy, data ownership, and rights related to digital content.
International Collaborations and Global Standards
Developing International Legal Frameworks for the Metaverse:
One major challenge in managing content in the metaverse is cultural and legal differences between countries. To address this, there is a need for international legal frameworks and global standards that all metaverse platforms must adhere to. International collaborations can unify these regulations and resolve conflicts arising from legal discrepancies across nations.
Supporting Global Research and Information Sharing:
Metaverse platforms should actively participate in global research and share their insights with international organizations in areas like law, security, and ethics. Such information exchange can improve existing solutions and propose new approaches for better metaverse content management.
Charts and Graphs
Chart 1: Growth of the Metaverse Market by 2027
This chart predicts the financial growth and number of users in the metaverse from 2023 to 2027, showcasing exponential growth due to increased users and large-scale investments.
- Horizontal axis: Years (2023–2027).
- Vertical axis: Market value (billion USD).
- Data:
- 2023: $70 billion.
- 2024: $100 billion.
- 2025: $140 billion.
- 2026: $200 billion.
- 2027: $280 billion.
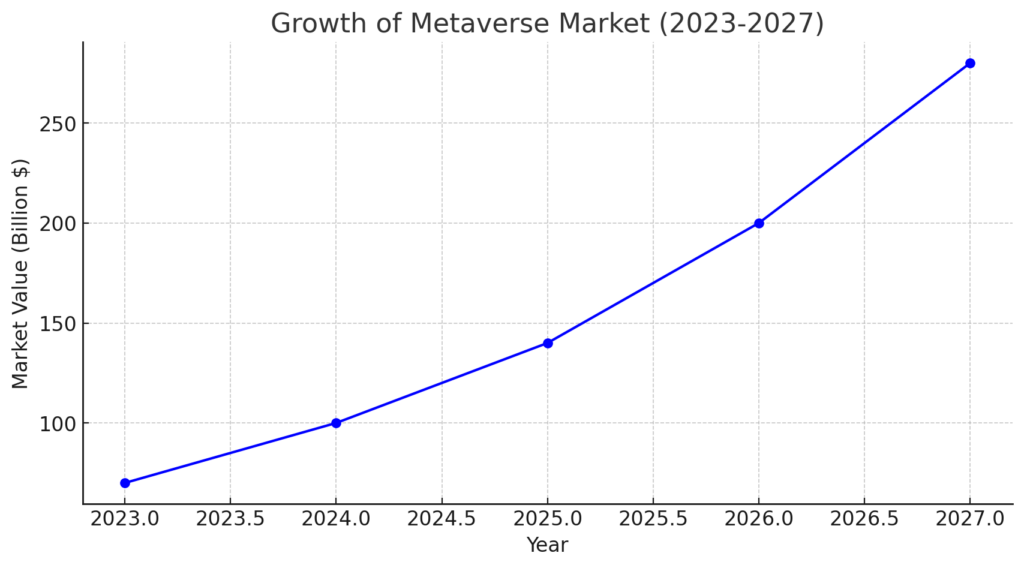
Metaverse Market Growth (2023-2027): Represents the Growth in the financial value of this field over the next five years
Chart 2: Distribution of Harmful Content in the Metaverse
This pie chart illustrates the proportion of various types of harmful content in metaverse environments.
- Sections:
- Cybercrimes: 35%.
- Virtual harassment: 25%.
- Misinformation: 20%.
- Violent content: 15%.
- Other: 5%.
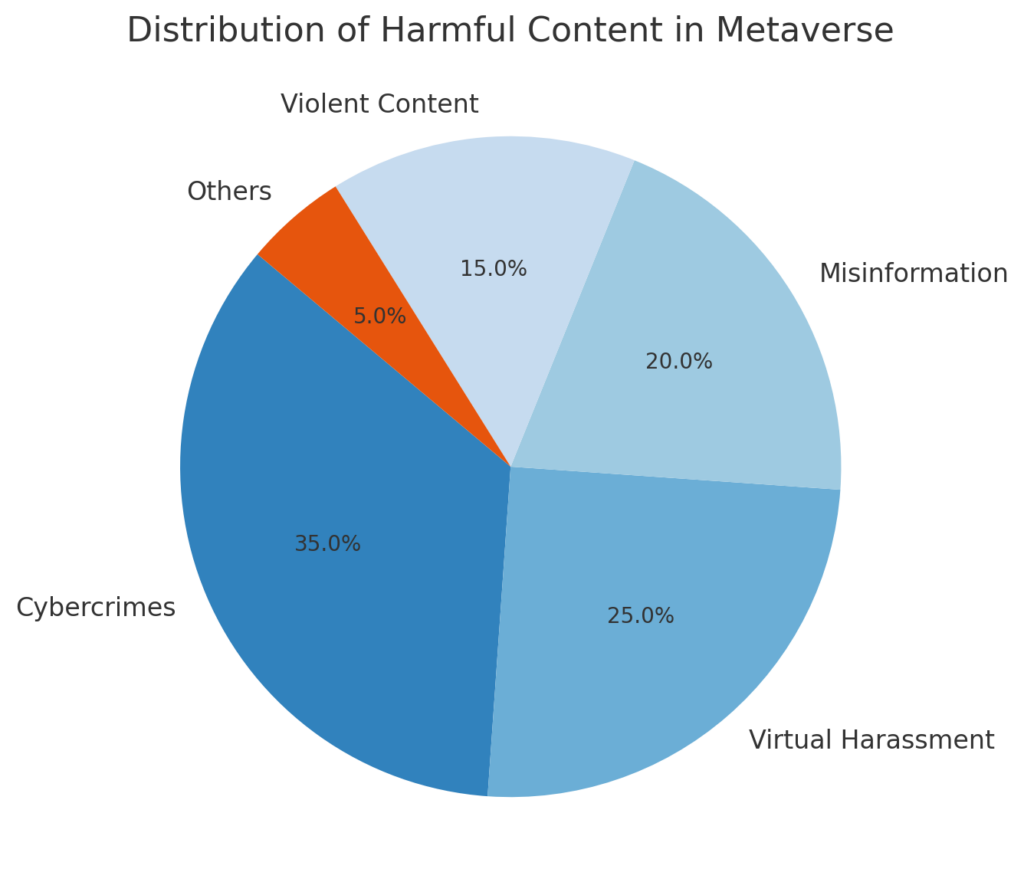
Distribution chart of harmful content in the metaverse: showing the proportion of harmful content types such as cybercrime and misinformation.
Chart 3: Comparison of Centralized and Decentralized Architectures
This comparative chart highlights key features of centralized and decentralized architectures in the metaverse.
- Horizontal axis: Metrics (privacy, security, transparency, operational costs).
- Vertical axis: Performance level (score 0–10).
- Data:
Centralized architecture:
Privacy: 4.
Security: 6.
Transparency: 3.
Operational costs: 8.
Decentralized architecture:
Privacy: 8.
Security: 9.
Transparency: 7.
Operational costs: 5.
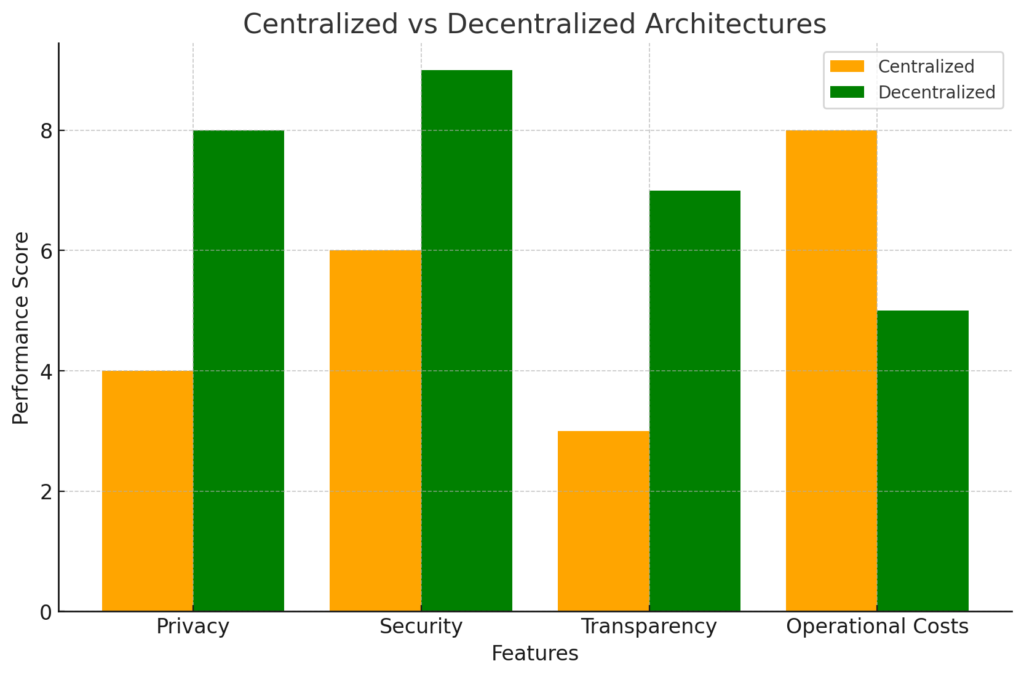
Centralized and decentralized architecture comparison chart: Examining the performance of these two types of architectures in key features.
Chart 4: Content Management Tools
This bar chart compares the effectiveness of various content management tools.
- Horizontal axis: Tools (AI, user reporting, big data analysis, manual methods).
- Vertical axis: Efficiency (%).
- Data:
AI: 85%.
User reporting: 60%.
Big data analysis: 75%.
Manual methods: 40%.
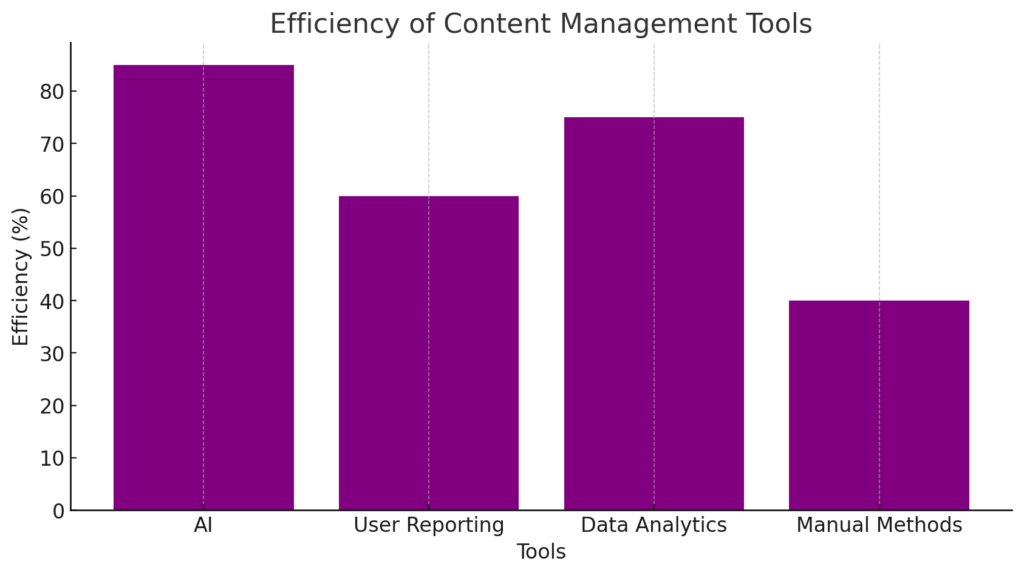
Content management tools chart: Comparing the effectiveness of different tools such as artificial intelligence and manual methods.
Chart 5: User Behavior in the Metaverse
This line chart reflects behavioral changes in users based on activity types in the metaverse.
- Horizontal axis: Activities (social interactions, trading, gaming, education, creative activities).
- Vertical axis: User engagement (%).
- Data:
- Social interactions: 40%.
- Trading: 25%.
- Gaming: 20%.
- Education: 10%.
- Creative activities: 5%.
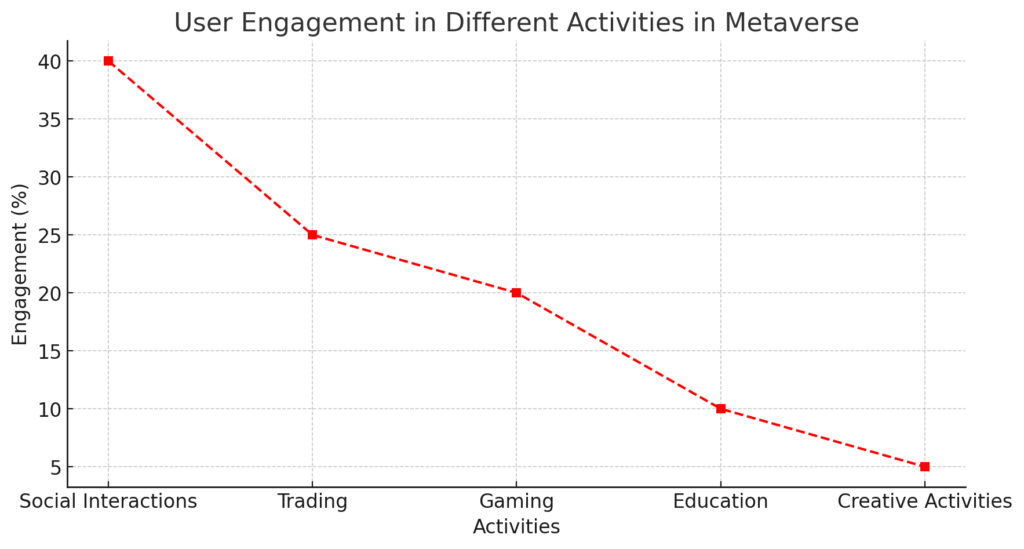
Metaverse user activity graph: Analyze user behavior in various sectors such as social interactions and education.
Future Outlook
The Foresight section looks at predictions, future innovations, and social developments related to the metaverse. As an emerging and dynamic phenomenon, the metaverse continues to develop, and we can expect major changes in the way humans interact with this virtual world, businesses, and the laws that govern them in the near future. In this section, we examine key predictions and innovations.
Predictions
Growth in Blockchain and AI Technologies:
Current trends suggest that blockchain and AI technologies will play a vital role in advancing the metaverse. Blockchain, as a decentralized technology, can enhance the metaverse’s stability and security while facilitating digital asset transfers, thereby increasing user trust.
AI will also be increasingly used for analyzing large-scale data and predicting user behavior. This technology can offer more personalized experiences and create automated, intelligent systems for identifying harmful content and managing metaverse spaces.
Increased Complexity of Content in the Metaverse
In the near future, the quality and complexity of metaverse content will significantly improve. This content will include realistic experiences, advanced simulations, and deeper interactions between users and avatars. Progress in VR and AR technologies will make these contents highly immersive, resembling real-world interactions.
Emerging technologies like 3D imaging, motion capture, and advanced animation will further enhance the realism of digital avatars and virtual environments, benefiting industries such as gaming, education, and healthcare.
The Expansion of Metaverses into Healthcare, Education, and Culture
One of the key predictions about the future of the metaverse is its expansion beyond entertainment and online gaming into other sectors such as healthcare, education, and culture. In these areas, the metaverse can bring about significant transformations:
- Healthcare: The metaverse can revolutionize fields like telemedicine and simulated surgeries. Doctors and surgeons can leverage metaverse environments for surgical simulations and medical training.
- Education: The metaverse can create fully virtual and interactive educational environments. Students can engage actively and practically in these spaces, particularly in specialized fields like engineering, medicine, and visual arts.
- Culture: The metaverse can serve as a cultural platform for showcasing art and historical heritage. Artists and researchers can create and share digital artworks, while virtual museums and galleries enable global audiences to explore exhibits from anywhere.
Future Innovations
Designing More Scalable and User-Friendly Metaverses
In the future, metaverses will become significantly more scalable and user-friendly. One of the current challenges is scalability, especially when millions of users access these environments simultaneously, leading to issues like latency or quality degradation. However, advancements in cloud infrastructure and distributed computing technologies are expected to alleviate these challenges substantially.
Additionally, metaverse user interfaces are continuously improving. Emerging systems based on voice and gesture interactions, rather than traditional keyboard and mouse inputs, will make digital experiences more natural and human-centric.
2. Global Regulations for Safer Metaverses
Given the complexities and regulatory challenges in the metaverse, significant changes in global laws and regulations are anticipated. Currently, many countries lack specific regulations for metaverse oversight, potentially leading to issues concerning privacy, cybersecurity, and digital ownership.
Governments and international organizations are expected to establish legal frameworks and global regulations to ensure user safety and mitigate potential risks. These regulations may cover data protection, monitoring illegal content, and defining digital ownership rights.
3. Transformations in Human Interactions with Metaverse Technologies
In the future, human interactions in the metaverse will evolve significantly. The metaverse is expected to integrate into daily life, serving as a substitute for many physical and social interactions. This will be particularly valuable in situations where in-person communications are limited or impossible.
The metaverse’s future could profoundly impact social interactions, allowing individuals to connect through digital avatars in virtual environments rather than meeting face-to-face. This trend became evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting how virtual spaces can replace physical events and gatherings.
Social Innovations
Innovative Methods to Support User Well-Being in the Metaverse
One notable future development is the creation of innovative methods to support the psychological and social well-being of metaverse users. In highly interactive online environments, users may face significant psychological and social pressures.
Innovative approaches, such as AI systems capable of identifying signs of depression or anxiety in online behaviors, can play a crucial role in addressing these issues. These systems could help users recognize and address their mental health challenges effectively.
2. Processes to Manage Social and Cultural Changes
As the metaverse expands, it will shape numerous social and cultural changes. However, these changes may also lead to challenges such as cultural clashes or a lack of harmony among individuals from diverse backgrounds. Thus, processes to manage these changes will become essential.
Organizations and metaverse platforms should aim to create inclusive environments that respect diverse cultures and identities. This could involve promoting digital cultural awareness, respecting others’ rights, and implementing monitoring systems to prevent biases or cultural discrimination.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the metaverse, as an emerging and advanced digital space, presents significant challenges in content management, regulations, and oversight. Achieving a balance between freedom of expression and user protection requires new standards, effective laws, and advanced technologies. Through international collaboration and the use of AI and modern tools, the metaverse can become a safer and more responsible environment for all users.
Table of Contents
Toggle

