Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Definition of the Metaverse and its Importance
- Introduction to Edge Computing and its Rationale for Use in the Metaverse
- Challenges in Real-Time Interactions and the Role of Edge Computing in Overcoming Them
- Objectives of the Paper
- Fundamental Concepts
- Edge Computing: Definition and its Differences from Cloud Computing
- Benefits of Edge Computing for the Metaverse
- The Metaverse: Concepts, Features, and Applications
- Key Features of the Metaverse
- Applications of the Metaverse
- The Importance of Combining Edge Computing and the Metaverse
- References
Abstract
In the digital age, where the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds are increasingly fading, the Metaverse stands as one of the most significant technological innovations, opening new paths for social, economic, and cultural interactions. However, to fully realize the potential of the Metaverse, several fundamental challenges must be overcome, such as delays in interactions, high data volumes, and the need for fast and effective information processing. Edge Computing, as an innovative solution, plays a key role in addressing these challenges by moving data processing closer to the sources of data generation.
This paper provides a comprehensive examination of the application of Edge Computing in the Metaverse, analyzing its impact on the speed and accuracy of real-time interactions. Key concepts of Edge Computing and the Metaverse are introduced, followed by a discussion of how this technology improves Metaverse performance through reduced latency, enhanced network efficiency, and personalized user experiences. Additionally, supporting technologies such as 5G networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), Edge AI, and blockchain are discussed as critical components in strengthening the Metaverse infrastructure.
The paper also explores significant challenges such as data security, infrastructure scalability, and resource management, offering solutions for overcoming these issues. Furthermore, examples of successful applications of Edge Computing in the Metaverse, including industrial and educational projects, are highlighted to demonstrate the emerging opportunities for this technology across various industries.
Finally, future research is suggested for the development of optimization algorithms and the integration of emerging technologies. This paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers and industry professionals, providing a deeper understanding of the importance of Edge Computing in advancing the Metaverse and outlining potential avenues for future research and innovation.

Introduction
- Definition of the Metaverse and its Importance
The Metaverse is defined as an immersive, three-dimensional digital world that blends Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms. This concept was first introduced in Neal Stephenson’s 1992 science fiction novel Snow Crash and has since become a central focus in technology research and development. 【1†source】【2†source】After the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for virtual and digital interactions skyrocketed, leading to the Metaverse emerging as an innovative solution to fulfill these needs.
The Metaverse is not only a virtual space for entertainment and gaming but also serves as a platform for education, commerce, healthcare, and social interactions. Imagine a virtual classroom where students from across the globe attend lessons, or a business meeting conducted in an interactive, three-dimensional environment. These possibilities make the Metaverse a revolutionary force in how humans and organizations interact.
- Introduction to Edge Computing and its Rationale for Use in the Metaverse
The Metaverse, as a complex ecosystem, requires real-time, high-volume data processing. Sending this data to central servers for processing creates significant latency, which can negatively affect user experience. Edge Computing, as a critical solution, addresses this issue by moving data processing closer to the data sources, such as sensors, IoT devices, and local servers. This approach reduces latency, improves processing speed, and enhances network efficiency. In the Metaverse, Edge Computing enables complex applications such as 3D rendering, real-time data analytics, and dynamic interactions.
- Challenges in Real-Time Interactions and the Role of Edge Computing in Overcoming Them
One of the most significant challenges facing the Metaverse is the need for real-time, interactive experiences. Users expect virtual environments to respond as quickly as the real world. However, this goal is hindered by issues such as network latency, bandwidth limitations, and the need to process large data volumes. Edge Computing serves as an effective solution, overcoming these challenges by processing tasks closer to the network edge, ensuring faster data processing and delivery to users. For example, in a virtual reality game requiring dynamic and real-time interactions, Edge Computing ensures that user movements are reflected in the virtual environment without delay.
【1†source】【2†source】

Objectives of the Paper
This paper aims to explore the applications of Edge Computing in the Metaverse and analyze its role in enhancing the speed, accuracy, and quality of real-time interactions. Supporting technologies such as 5G, IoT, Edge AI, and blockchain, along with existing challenges and emerging opportunities in this domain, will be discussed. Finally, the paper will propose future research pathways and innovative solutions for advancing the Metaverse.
Fundamental Concepts
- Edge Computing: Definition and its Differences from Cloud Computing
Edge Computing is one of the most advanced computational models, transferring data processing closer to the data source. Unlike cloud computing, which sends data to centralized data centers for processing, Edge Computing uses local devices, edge servers, or even sensors to process and store data. This approach significantly reduces latency, improves responsiveness, and enhances efficiency in complex systems like the Metaverse. 【1†source】【2†source】
Key differences between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing include:
- Cloud Computing: Data is sent to centralized servers for processing and returned as results. This model is suitable for heavy but non-urgent processing tasks.
- Edge Computing: Data is processed near its source, reducing the need for data transmission to centralized servers, improving response times, and reducing delays.
These features make Edge Computing ideal for environments requiring real-time interactions, such as the Metaverse.
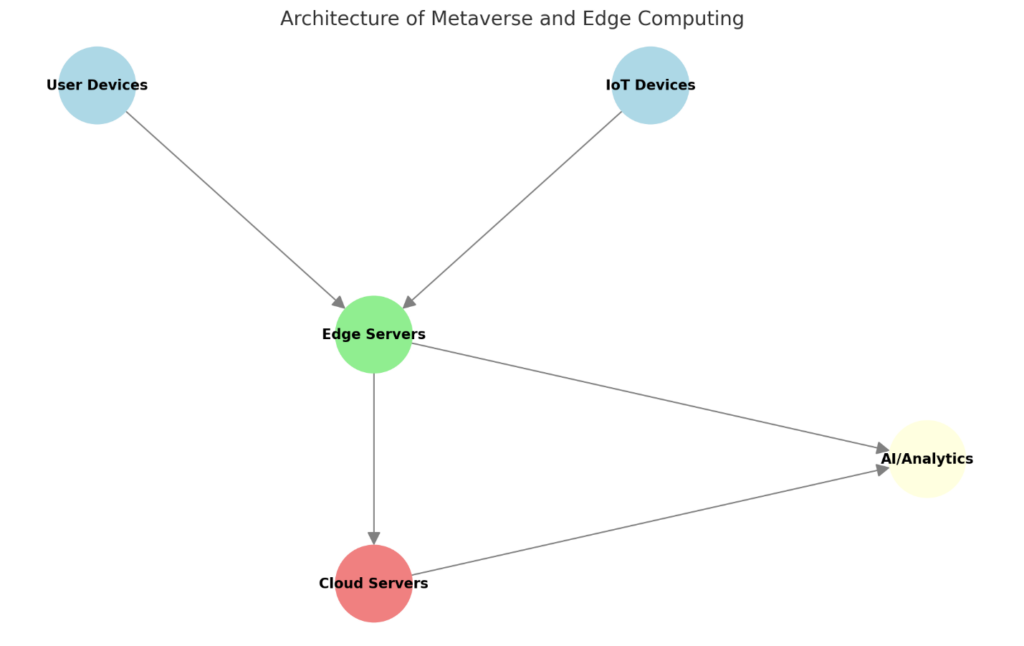
This diagram illustrates the architecture of the Metaverse and Edge Computing system. In this structure:
- User Devices: Refers to devices such as mobile phones, VR headsets, and user computers.
- IoT Devices: Includes sensors and connected devices for data collection and transmission.
- Edge Servers: Responsible for processing data close to its source to minimize latency.
- Cloud Servers: Handle heavy processing and data storage in centralized data centers.
- AI/Analytics: Provide real-time analysis and personalization based on processed data.
- Advantages of Edge Computing for the Metaverse
- Reduced Latency: Interactions in the Metaverse require extremely short response times. Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data closer to users.
- Reduced Network Load: Transmitting large volumes of data to central data centers can overwhelm network bandwidth. Edge computing performs initial processing locally, sending only essential data to the cloud.
- Improved User Experience: Local processing ensures a smoother, uninterrupted experience for Metaverse users.
- Latency Comparison Between Edge and Cloud Computing
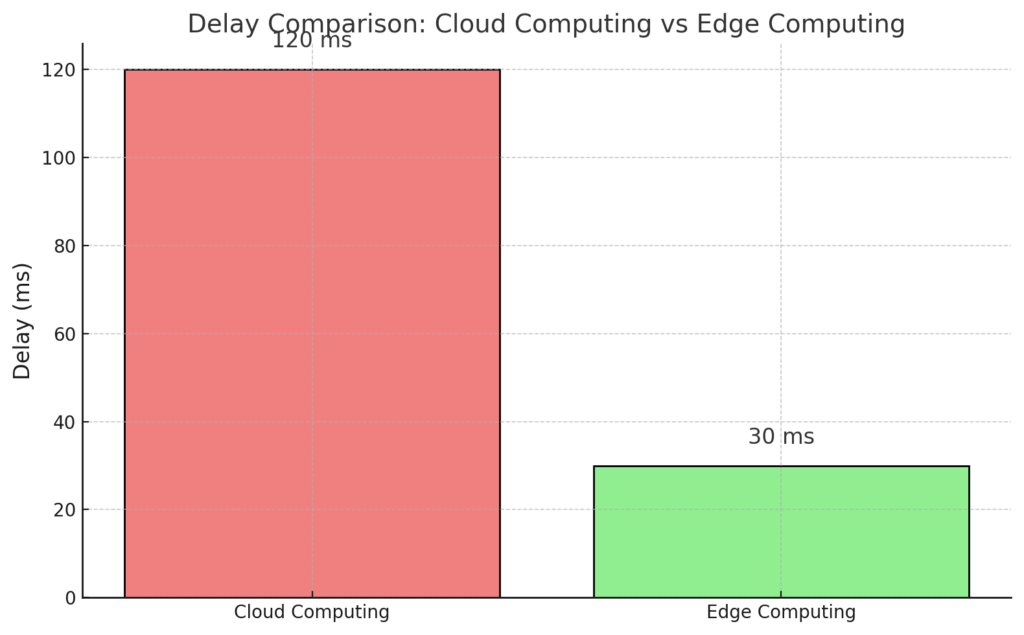
This graph compares data processing latency between cloud computing and edge computing:
- Cloud Computing: Higher latency due to the need for transmitting data to central processing centers.
- Edge Computing: Lower latency as data is processed near its source.
This reduction in latency plays a critical role in enhancing the user experience in the Metaverse.
Metaverse: Concepts, Features, and Applications
The Metaverse is defined as a shared digital space that combines virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and the physical world. This interactive environment leverages technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain to create an immersive experience.
- Key Features of the Metaverse
- Real-Time Interactions: Users can interact with others and the environment using digital avatars in real time.
- Digital Ownership: Blockchain enables identification and transfer of virtual assets like NFTs within the Metaverse.
- Personalized Experiences: AI analyzes user behavior to deliver tailored experiences.
- Applications of the Metaverse
- Education: Offers interactive learning environments, such as lab simulations or 3D classrooms.
- Entertainment: Hosts concerts, sports events, and VR games.
- Healthcare: Provides VR therapies for rehabilitation or stress reduction.
- Commerce and Economy: Enables buying and selling digital assets, hosting business meetings, and fostering a virtual economy.
The Importance of Combining Edge Computing and the Metaverse
The integration of edge computing with the Metaverse is essential due to the technical and functional demands of this space. On one hand, real-time data processing is vital for seamless and dynamic interactions; on the other hand, edge computing reduces data transfer costs and bandwidth usage, offering a competitive advantage.
Examples:
- In a multiplayer VR game, edge computing can process players’ motion data locally and share results with other users, ensuring a synchronized and realistic experience.
- In educational Metaverse environments, processing students’ interactive data locally reduces latency, enhancing the learning experience. 【1†source】【2†source】
References
- Patra, A., Pandey, A., Hassija, V., Chamola, V., & Mishra, R. P. (2024). A Survey on Edge Enabled Metaverse: Applications, Technological Innovations, and Prospective Trajectories. IEEE Access. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3452184
- Hatami, M., Qu, Q., Chen, Y., Kholidy, H., Blasch, E., & Ardiles-Cruz, E. (2024). A Survey of the Real-Time Metaverse: Challenges and Opportunities. Future Internet. DOI: 10.3390/fi16100379
Table of Contents
Toggle


One Response