- Introduction
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Specialized tools for Augmented Reality
- Applications of AR
- Collaborative Virtual Reality
- Specialized tools for Collaborative Virtual Reality
- Applications of MR
- Medical Virtual Reality
- Specialized tools for Medical Virtual Reality
- Applications of Medical VR
- Future advancements and challenges in VR
- Increased realism with the help of AI and machine learning
- 5G networks and enhanced quality of VR experiences
- Challenges related to physical and mental health of users
- High costs of equipment and limited accessibility
- Need for increased security and privacy
- Designing multi-purpose and interactive content
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the previous article, we discussed the applications of virtual reality and its three main categories. In the second part of the VR technology article, we will examine 4 subcategories of VR, including Augmented Reality, Collaborative Virtual Reality, Mixed Reality, and Medical Virtual Reality.
Augmented Reality (AR)
The fourth category is a form of augmented reality. Augmented Reality (AR) allows the user to observe the real world using a device and add virtual elements to it. In this technology, virtual information is added to the real image, which can include texts, 3D shapes, images, and even interactive videos. Augmented Reality is a type of Virtual Reality where the user sees the virtual world through a phone screen and applies virtual changes to it. Augmented Reality is when an entity or specific device exists in reality but does not actually exist, and instead of immersing you in the virtual world, it places a virtual entity in the real world through any tool. A good example of it is the game Pokémon Go. This game is made in the style of Augmented Reality. In this game, you turn on your phone’s camera and aim it toward a place where you guess a Pokémon might be, and once your phone shows the Pokémon on your screen, you see it as if it were in a frame. Pokémon only appears on your display screen, and there is no physical addition to the real environment where you are filming. Another application is in the design industry for various places. Suppliers of home and office furnishings or decorators use this technology.
- Specialized tools for Augmented Reality
- Depth-Sensing Cameras
These cameras use specialized sensors to measure the depth and distance of objects. This capability is crucial for accurately and naturally placing virtual objects on the real image.
- AR headsets and portable devices
Headsets like Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap allow the user to view virtual images and information directly in their environment.
- AR-specific software and engines
Among these software tools are ARKit (for iOS) and ARCore (for Android), which enable the development and creation of interactive AR content.
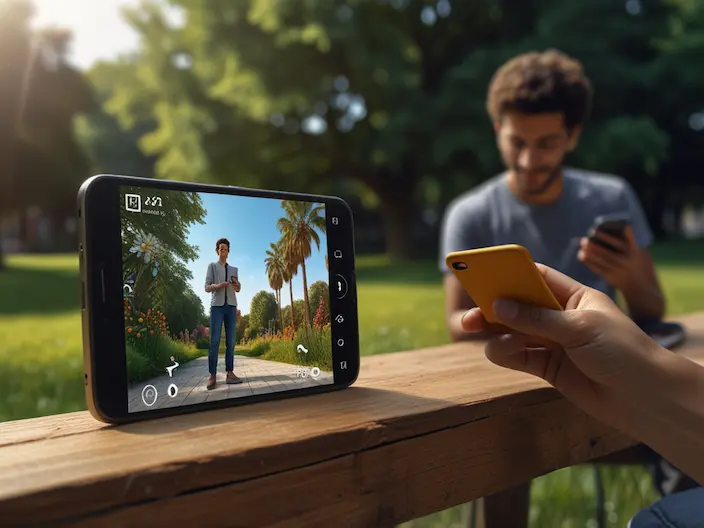

- Applications of AR
- Interior design and education industry
In this industry, augmented reality is used for interior design, layout of decoration, and creating interactive environments. Companies like IKEA have provided programs that allow users to virtually test various items in their homes.
- E-commerce and marketing
AR enables stores and brands to provide a distinct and interactive experience for their customers. For example, with AR applications, customers can virtually try on clothes or makeup.
Collaborative Virtual Reality
The fifth category is Collaborative Virtual Reality, where users from different locations can gather in a virtual environment as 3D avatar-like characters, allowing them to interact from various locations in a virtual environment as avatars. This type of VR is particularly useful for applications such as group training, business meetings, and multiplayer games. An example of this is the mobile game PlayerUnknown’s BattleGrounds (PUBG). In this game, various 3D and virtual characters come together, interacting with each other’s virtual characters through microphone, headset, and chat. Other examples include holding remote virtual business meetings, training, or virtual debate competitions. The main goal of this VR category is to foster collaboration among people.
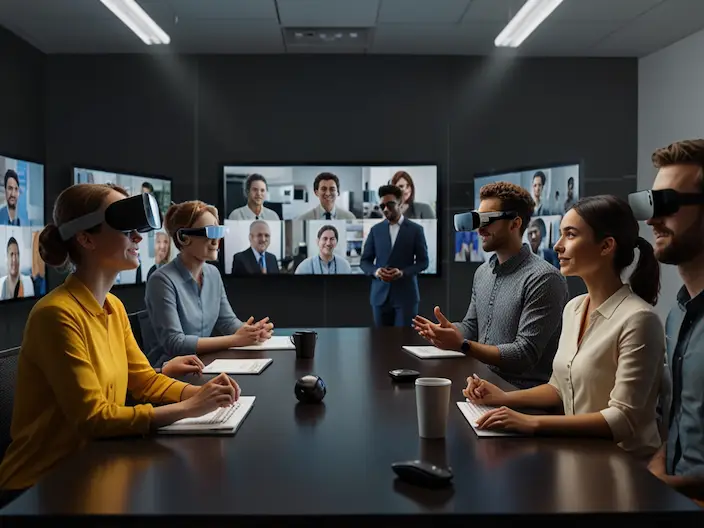

- Specialized tools for Collaborative Virtual Reality
- VR headsets with networking and multiplayer interaction capabilities
For collaborative experiences, headsets like the Oculus Quest and HTC Vive Pro that support networking features are used.
- Collaborative VR platforms
Platforms like AltspaceVR, VRChat, and Rec Room allow users to interact and converse with each other as virtual avatars.
- Applications of Collaborative VR
- Conducting business meetings and conferences
Companies can hold their meetings in a three-dimensional and realistic environment instead of in-person meetings or video conferences.
- Education and simulation
In medical, industrial, and military training, collaborative VR allows users to participate in interactive exercises simultaneously and remotely.
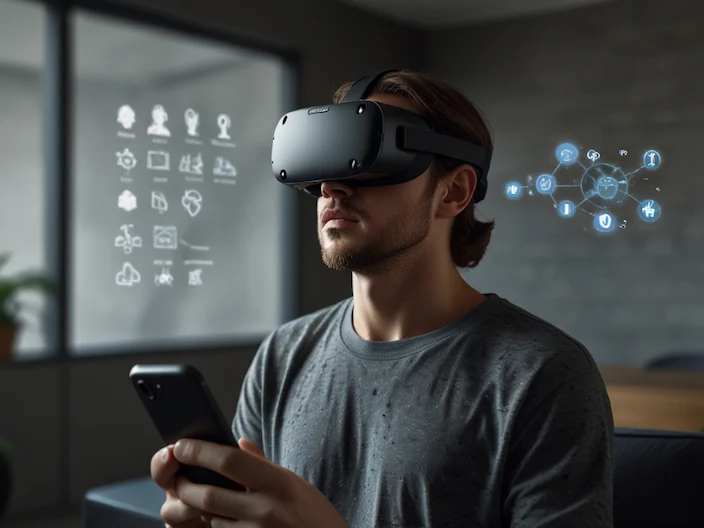

Mixed Reality (MR)
The sixth category is Mixed Reality, one of the latest advancements in the VR field. Mixed Reality (MR) is newer technology that combines virtual elements interactively with the real world. Unlike augmented reality, in MR, virtual and real elements can interact with each other. Unlike AR, in MR, virtual components interact with the real world. As a result, the VR experience is truly affected. MR is the integration of the real and virtual worlds, where physical and digital objects coexist and interact in real-time. For example, surgeons place virtual ultrasound images on their patient during surgery. The key feature of MR is that artificial and real-world content can react to each other in real-time. People can use MR to interact with 3D holograms in comfortable physical environments like their living rooms using technologies such as Microsoft HoloLens. Immersive tours and demonstrations have been created by MR, allowing students to gain a complete understanding of various concepts. Companies can also use MR applications to create engaging team-building exercises for their employees, which are essential for building strong relationships within the team.
- Specialized tools for Mixed Reality
- MR headsets
Devices like the HoloLens and Magic Leap One, which use advanced sensors to interact with the real environment.
- Environmental sensors and 3D interaction software
These sensors and software can detect changes in the real environment and update virtual elements based on them.

- Applications of MR
- Medicine and complex surgeries
With the help of mixed reality, surgeons can precisely view 3D models of the patient’s organs on their body.
- Interactive education and scientific simulations
MR enables students and researchers to engage more realistically with scientific concepts and complex experiments.
Medical Virtual Reality (VR)
The seventh category is medical virtual reality. This is one of the most specialized applications of VR in the medical field. In this category, simulations and virtual environments allow doctors and medical staff to practice and enhance their skills in a safe environment. In the field of medicine, VR is used for many purposes, to the extent that it can be considered its own category of virtual reality. In businesses where precision and finesse are paramount and critical approaches to problems are essential, virtual environments offer significant benefits. One of the most evident advantages is that doctors and nurses can immerse themselves in simulations during their training in a safe setting. For example, they can learn to perform real-time surgeries through VR training. These environments vary depending on the profession within the medical field and, by providing human and animal anatomy, they help users better understand their work conditions. Beyond the VR in the medical sector, patients requiring rehabilitation, mental treatments, and others can benefit from this segment of virtual reality.
- Specialized VR Tools for Medicine
- VR Surgical Simulators
Special headsets and software, such as Osso VR and Touch Surgery, enable doctors to simulate complex surgeries.
- Rehabilitation and Therapeutic Equipment Using VR
Devices equipped with headsets and motion sensors assist patients in rehabilitation and recovery phases.
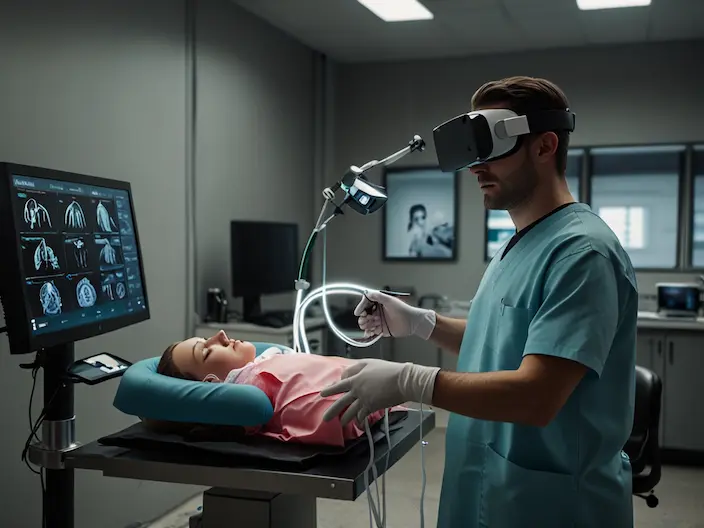
- Medical VR Applications
- Surgical Training and Medical Simulations
VR enables doctors and medical students to practice through simulated exercises in virtual environments.
- Rehabilitation and Psychotherapy Treatments
VR helps patients engage in rehabilitation and psychotherapy in a calm and controlled environment.
Future Advancements and Challenges in VR
Virtual reality technology (VR) continues to evolve and expand, with new applications and capabilities emerging every day. Despite remarkable advancements, there are still significant challenges facing this technology, which are discussed below. Issues such as high equipment costs, the need for appropriate physical space, and the long-term effects of VR on human health remain points of concern.
- Increasing Realism with AI and Machine Learning
One of VR’s primary goals is to enhance realism and allow for natural interaction with virtual environments. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in VR has enabled systems to analyze user behavior accurately and adjust virtual responses to appear entirely natural. For instance, AI can create interactive avatars with more realistic capabilities and intelligent personalities, capable of interacting with users coherently and convincingly. These advancements will significantly impact fields such as virtual reality gaming, simulation-based training, and even psychological therapies.
- 5G Networks and Enhanced VR Experiences
5G networks bring a transformative improvement in data transfer and latency reduction, which directly influences VR experiences. With increased internet speeds and reduced delays, users can benefit from broader virtual environments and more complex interactive experiences. 5G plays a substantial role in the development and expansion of collaborative VR, as it allows people from different locations to connect without delay. This technology enables companies to hold large meetings and events in VR spaces, allowing users to participate without interruption.

- Physical and Mental Health Challenges for Users
Although VR experiences have numerous advantages, they may have negative effects on users’ health. VR nausea, or motion sickness, resulting from discrepancies between head movements and virtual images, is a serious challenge for this technology. Studies indicate that prolonged use of VR headsets can lead to increased eye strain, reduced concentration, and sleep disorders. Furthermore, some users may develop an addiction to virtual reality, which can negatively impact their social relationships and mental health. Addressing these challenges requires the development of improved headsets with faster adaptation capabilities and reduced delays between actual movements and virtual imagery.
- High Equipment Costs and Limited Access
Although the production costs for VR headsets and tools have decreased in recent years, they are still expensive for the general public. In addition to headsets, users often require additional hardware such as powerful computers and adequate physical space to use VR. These limitations, especially in developing countries or communities with lower incomes, restrict access to this technology and impact VR’s growth.
- Need for Enhanced Security and Privacy
VR technology, due to its use of personal data and user movements, has raised critical security and privacy issues. Given that VR collects data related to body movements and even facial details, securing this information is vital. If this data falls into the hands of strangers or hackers, it could threaten users’ security. VR companies need to offer stronger solutions for data protection and ensure users’ privacy is safeguarded.

- Designing Multifunctional and Interactive Content
A key challenge in VR is creating content that meets the diverse needs of users. Producing interactive and comprehensive content for a wide range of applications, such as education, entertainment, health, and commerce, requires substantial budget and time. Additionally, it should be considered that virtual experiences must be designed to be equally appealing and usable for both novice and professional users. VR content developers can foster the growth of this technology and attract more users by creating more creative and flexible tools.
Conclusion
Despite its challenges, virtual reality technology is recognized as one of the 21st century’s greatest innovations, capable of revolutionizing many fields. New advancements in 5G networks, artificial intelligence, and the development of advanced headsets pave the way for more realistic experiences and broader applications. However, the success of this technology depends on addressing security, physical and mental health, and universal accessibility challenges. If various industries can collaborate with researchers and developers to properly manage these issues, VR has a bright future ahead, where it will be embraced as an integral part of daily and professional life.
Table of Contents
Toggle


One Response